Tensor
tensorflow C++ API
Represents an n-dimensional array of values.
Public functions
AllocatedBytes
size_t AllocatedBytes() const
AsProtoField
void AsProtoField(
TensorProto *proto
) const
Fills inprotowith*thistensor’s content.
AsProtoField()fills in the repeated field forproto.dtype(), whileAsProtoTensorContent()encodes the content inproto.tensor_content()in a compact form.
AsProtoTensorContent
void AsProtoTensorContent(
TensorProto *proto
) const
CopyFrom
bool CopyFrom(
const Tensor & other,
const TensorShape & shape
) TF_MUST_USE_RESULT
Copy the other tensor into this tensor and reshape it.
This tensor shares other’s underlying storage. Returnstrueiffother.shape()has the same number of elements of the givenshape.
DebugString
string DebugString() const
A human-readable summary of the tensor suitable for debugging.
FillDescription
void FillDescription(
TensorDescription *description
) const
Fill in theTensorDescriptionproto with metadata about the tensor that is useful for monitoring and debugging.
FromProto
bool FromProto(
const TensorProto & other
) TF_MUST_USE_RESULT
Parseotherand construct the tensor.
Returnstrueiff the parsing succeeds. If the parsing fails, the state of*thisis unchanged.
FromProto
bool FromProto(
Allocator *a,
const TensorProto & other
) TF_MUST_USE_RESULT
IsAligned
bool IsAligned() const
Returns true iff this tensor is aligned.
IsInitialized
bool IsInitialized() const
If necessary, has this Tensor been initialized?
Zero-element Tensors are always considered initialized, even if they have never been assigned to and do not have any memory allocated.
IsSameSize
bool IsSameSize(
const Tensor & b
) const
NumElements
int64 NumElements() const
Convenience accessor for the tensor shape.
SharesBufferWith
bool SharesBufferWith(
const Tensor & b
) const
Slice
Tensor Slice(
int64 dim0_start,
int64 dim0_limit
) const
Slice this tensor along the 1st dimension.
I.e., the returned tensor satisfies returned[i, …] == this[dim0_start + i, …]. The returned tensor shares the underlying tensor buffer with this tensor.
NOTE: The returned tensor may not satisfies the same alignment requirement as this tensor depending on the shape. The caller must check the returned tensor’s alignment before calling certain methods that have alignment requirement (e.g.,flat(),tensor()).
REQUIRES:dims()>= 1 REQUIRES:0 <= dim0_start <= dim0_limit <= dim_size(0)
SummarizeValue
string SummarizeValue(
int64 max_entries
) const
Render the firstmax_entriesvalues in*thisinto a string.
Tensor
Tensor()
Creates a 1-dimensional, 0-element float tensor.
The returned Tensor is not a scalar (shape {}), but is instead an empty one-dimensional Tensor(shape {0}, NumElements() == 0). Since it has no elements, it does not need to be assigned a value and is initialized by default (IsInitialized() is true). If this is undesirable, consider creating a one-element scalar which does require initialization:
```c++
Tensor(DT_FLOAT, TensorShape({}))
```
Tensor
Tensor(
DataType type,
constTensorShape & shape
)
Creates a Tensor of the giventypeandshape.
If LogMemory::IsEnabled() the allocation is logged as coming from an unknown kernel and step. Calling the Tensor constructor directly from within an Op is deprecated: use the OpKernelConstruction/OpKernelContext allocate_* methods to allocate a new tensor, which record the kernel and step.
The underlying buffer is allocated using aCPUAllocator.
Tensor
Tensor(
Allocator *a,
DataType type,
const TensorShape & shape
)
Creates a tensor with the inputtypeandshape, using the allocatorato allocate the underlying buffer.
If LogMemory::IsEnabled() the allocation is logged as coming from an unknown kernel and step. Calling the Tensor constructor directly from within an Op is deprecated: use the OpKernelConstruction/OpKernelContext allocate_* methods to allocate a new tensor, which record the kernel and step.
amust outlive the lifetime of this Tensor.
Tensor
Tensor(
Allocator *a,
DataType type,
const TensorShape & shape,
const AllocationAttributes & allocation_attr
)
Creates a tensor with the inputtypeandshape, using the allocatoraand the specified “allocation_attr” to allocate the underlying buffer.
If the kernel and step are known allocation_attr.allocation_will_be_logged should be set to true and LogMemory::RecordTensorAllocation should be called after the tensor is constructed. Calling the Tensor constructor directly from within an Op is deprecated: use the OpKernelConstruction/OpKernelContext allocate_* methods to allocate a new tensor, which record the kernel and step.
amust outlive the lifetime of this Tensor.
Tensor
Tensor(
DataType type
)
Creates an empty Tensor of the given data type.
Like Tensor(), returns a 1-dimensional, 0-element Tensor with IsInitialized() returning True. See the Tensor() documentation for details.
Tensor
Tensor(
const Tensor & other
)
Copy constructor.
Tensor
Tensor(
Tensor && other
)
Move constructor.
After this call,is safely destructible and can be assigned to, but other calls on it (e.g. shape manipulation) are not valid.
TotalBytes
size_t TotalBytes() const
Returns the estimated memory usage of this tensor.
UnsafeCopyFromInternal
void UnsafeCopyFromInternal(
const Tensor &,
DataType dtype,
const TensorShape &
)
Copy the other tensor into this tensor and reshape it and reinterpret the buffer’s datatype.
This tensor shares other’s underlying storage.
bit_casted_shaped
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::Tensor bit_casted_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice< int64 > new_sizes
)
Return the tensor data to anEigen::Tensorwith the new shape specified innew_sizesand cast to a new dtypeT.
Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations. The allowed bitcast is the only difference fromshaped().
bit_casted_shaped
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::ConstTensor bit_casted_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice< int64 > new_sizes
)const
Return the tensor data to anEigen::Tensorwith the new shape specified innew_sizesand cast to a new dtypeT.
Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations. The allowed bitcast is the only difference fromshaped().
bit_casted_tensor
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::Tensor bit_casted_tensor()
Return the tensor data to anEigen::Tensorwith the same size but a bitwise cast to the specified dtypeT.
Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations. NOTE: this is the same astensor()except a bitcast is allowed.
bit_casted_tensor
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::ConstTensor bit_casted_tensor() const
Return the tensor data to anEigen::Tensorwith the same size but a bitwise cast to the specified dtypeT.
Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations. NOTE: this is the same astensor()except a bitcast is allowed.
dim_size
int64 dim_size(
int d
) const
Convenience accessor for the tensor shape.
dims
int dims() const
Convenience accessor for the tensor shape.
For all shape accessors, see comments for relevant methods ofTensorShapeintensor_shape.h.
dtype
DataType dtype() const
Returns the data type.
flat
TTypes< T >::Flat flat()
Return the tensor data as anEigen::Tensorof the data type and a specified shape.
These methods allow you to access the data with the dimensions and sizes of your choice. You do not need to know the number of dimensions of theTensorto call them. However, theyCHECKthat the type matches and the dimensions requested creates anEigen::Tensorwith the same number of elements as the tensor.
Example:
```c++
typedeffloat T;
Tensor my_ten(...built withShape{planes:4, rows:3, cols:5}...);
// 1D Eigen::Tensor, size 60:
auto flat = my_ten.flat();
// 2D Eigen::Tensor 12 x 5:
auto inner = my_ten.flat_inner_dims();
// 2D Eigen::Tensor 4 x 15:
auto outer = my_ten.shaped({4,15});
// CHECK fails, bad num elements:
auto outer = my_ten.shaped({4,8});
// 3D Eigen::Tensor 6 x 5 x 2:
auto weird = my_ten.shaped({6,5,2});
// CHECK fails, type mismatch:
auto bad = my_ten.flat();
```
flat
TTypes< T >::ConstFlat flat() const
flat_inner_dims
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::Tensor flat_inner_dims()
Returns the data as an Eigen::Tensor with NDIMS dimensions, collapsing all Tensor dimensions but the last NDIMS-1 into the first dimension of the result.
If NDIMS > dims() then leading dimensions of size 1 will be added to make the output rank NDIMS.
flat_inner_dims
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::ConstTensor flat_inner_dims() const
flat_inner_outer_dims
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::Tensor flat_inner_outer_dims(
int64 begin
)
Returns the data as an Eigen::Tensor with NDIMS dimensions, collapsing the first ‘begin’ Tensor dimensions into the first dimension of the result and the Tensor dimensions of the last dims() - ‘begin’ - NDIMS into the last dimension of the result.
If ‘begin’ < 0 then the |‘begin’| leading dimensions of size 1 will be added. If ‘begin’ + NDIMS > dims() then ‘begin’ + NDIMS - dims() trailing dimensions of size 1 will be added.
flat_inner_outer_dims
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::ConstTensor flat_inner_outer_dims(
int64 begin
) const
flat_outer_dims
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::Tensor flat_outer_dims()
Returns the data as an Eigen::Tensor with NDIMS dimensions, collapsing allTensordimensions but the first NDIMS-1 into the last dimension of the result.
If NDIMS >dims()then trailing dimensions of size 1 will be added to make the output rank NDIMS.
flat_outer_dims
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::ConstTensor flat_outer_dims() const
matrix
TTypes< T >::Matrix matrix()
matrix
TTypes< T >::ConstMatrix matrix() const
operator=
Tensor & operator=(
const Tensor & other
)
Assign operator. This tensor shares other’s underlying storage.
operator=
Tensor & operator=(
Tensor && other
)
Move operator. See move constructor for details.
scalar
TTypes< T >::Scalar scalar()
Return the Tensor data as aTensorMapof fixed size 1:TensorMap>.
Usingscalar()allows the compiler to perform optimizations as the size of the tensor is known at compile time.
scalar
TTypes< T >::ConstScalar scalar() const
shape
const Tensor Shape& shape() const
Returns the shape of the tensor.
shaped
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::Tensor shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice< int64 > new_sizes
)
shaped
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::ConstTensor shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice< int64 > new_sizes
) const
tensor
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::Tensor tensor()
tensor
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::ConstTensor tensor() const
tensor_data
StringPiece tensor_data() const
Returns aStringPiecemapping the current tensor’s buffer.
The returnedStringPiecemay point to memory location on devices that the CPU cannot address directly.
NOTE: The underlying tensor buffer is refcounted, so the lifetime of the contents mapped by theStringPiecematches the lifetime of the buffer; callers should arrange to make sure the buffer does not get destroyed while theStringPieceis still used.
REQUIRES:DataTypeCanUseMemcpy(dtype()).
unaligned_flat
TTypes< T >::UnalignedFlat unaligned_flat()
unaligned_flat
TTypes< T >::UnalignedConstFlat unaligned_flat() const
unaligned_shaped
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::UnalignedTensor unaligned_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice< int64 > new_sizes
)
unaligned_shaped
TTypes< T, NDIMS >::UnalignedConstTensor unaligned_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice< int64 > new_sizes
) const
vec
TTypes< T >::Vec vec()
Return the tensor data as anEigen::Tensorwith the type and sizes of thisTensor.
Use these methods when you know the data type and the number of dimensions of the Tensor and you want anEigen::Tensorautomatically sized to theTensorsizes. The implementation check fails if either type or sizes mismatch.
Example:
```c++
typedeffloat T;
Tensor my_mat(...built withShape{rows:3, cols:5}...);
auto mat = my_mat.matrix();// 2D Eigen::Tensor, 3 x 5.
auto mat = my_mat.tensor();// 2D Eigen::Tensor, 3 x 5.
auto vec = my_mat.vec();// CHECK fails as my_mat is 2D.
auto vec = my_mat.tensor();// CHECK fails as my_mat is 2D.
auto mat = my_mat.matrix();// CHECK fails as type mismatch.
```
vec
TTypes< T >::ConstVec vec() const
Const versions of all the methods above.
~Tensor
~Tensor()
Tensor block
Source link :https://github.com/EXPNUNI/enuSpaceTensorflow/blob/master/enuSpaceTensorflow/tf_core.cpp
Argument:
- DataType
dtype: Types of Input Variables. ( DT_INT8, DT_INT16, DT_INT32,DT_INT64, DT_FLOAT, DT_DOUBLE etc….) - Input
initvalue: The value of the input variable. It can be written in python syntax. (ex: {1,2} -> shape: [2], input[1] = 1 input[2] = 2)
Output:
- Input
input: return Input type of tensor
UsingMethod
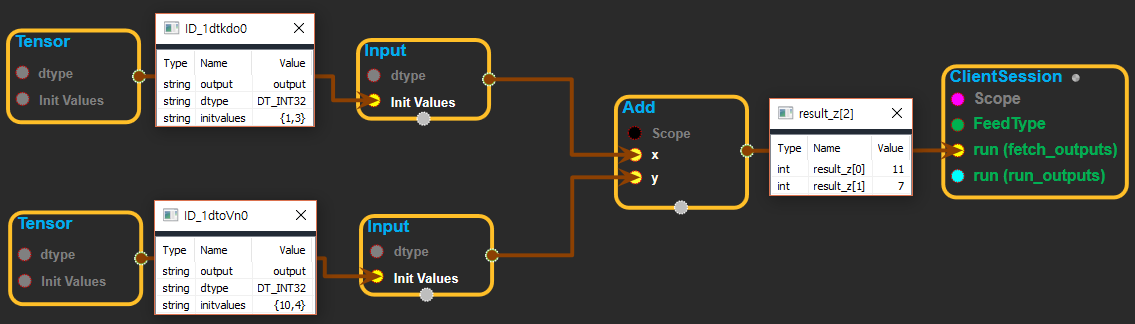 ※ tensor를 input에 연결하여 사용하는 화면
※ tensor를 input에 연결하여 사용하는 화면
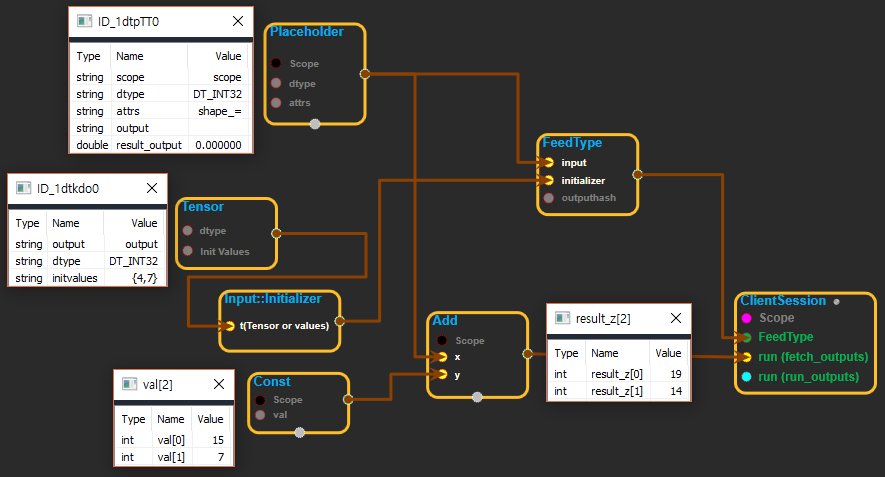 ※ tensor를 input::initializer에 연결하여 placeholder를 초기화 하는데 사용하는 화면
※ tensor를 input::initializer에 연결하여 placeholder를 초기화 하는데 사용하는 화면