StridedSliceGrad
tensorflow C++ API
tensorflow::ops::StridedSliceGrad
Returns the gradient of StridedSlice.
Summary
Since StridedSlice cuts out pieces of its input which is size shape, its gradient will have the same shape (which is passed here as shape). The gradient will be zero in any element that the slice does not select.
Arguments are the same as StridedSliceGrad with the exception that dy is the input gradient to be propagated and shape is the shape of StridedSlice’s input.
Arguments:
- scope: A Scope object
Returns:
Output: The output tensor.
StridedSliceGrad block
Source link :https://github.com/EXPNUNI/enuSpaceTensorflow/blob/master/enuSpaceTensorflow/tf_array_ops.cpp

Argument:
- Scope scope : A Scope object (A scope is generated automatically each page. A scope is not connected.)
- Input shape: A vector
Tensor. Determine the shape. - Input begin: An
int32orint64 Tensor. `begin[k]` specifies the offset into the `k`th range specification. The exact dimension this corresponds to will be determined by context. Out-of-bounds values will be silently clamped. If the `k`th bit of `begin_mask` then `begin[k]` is ignored and the full range of the appropriate dimension is used instead. Negative values causes indexing to start from the highest element e.g. If `foo==[1,2,3]` then `foo[-1]==3`. - Input end: An
int32orint64 Tensor. `end[i]` is like `begin` with the exception that `end_mask` is used to determine full ranges. - Input strides: An
int32orint64 Tensor. `strides[i]` specifies the increment in the `i`th specification after extracting a given element. Negative indices will reverse the original order. Out or range values are clamped to `[0,dim[i]) if slice[i]>0or[-1,dim[i]-1] if slice[i] < 0` - Input dy: A
Tensor. - StridedSlice::Attrs attrs:
- begin_mask: a bitmask where a bit i being 1 means to ignore the begin value and instead use the largest interval possible. At runtime begin[i] will be replaced with
[0, n-1) ifstride[i] > 0or[-1, n-1]ifstride[i] < 0 - end_mask: analogous to begin_mask
- shrink_axis_mask: a bitmask where bit i implies that the i th specification should shrink the dimensionality. begin and end must imply a slice of size 1 in the dimension. For example in python one might do foo[:, 3, :] which would result in shrink_axis_mask being 2.
- ellipsis_mask: a bitmask where bit i being 1 means the i`th position is actually an ellipsis. One bit at most can be 1. If ellipsis_mask == 0, then an implicit ellipsis mask of 1 << (m+1) is provided. This means that foo[3:5] == foo[3:5, …]. An ellipsis implicitly creates as many range specifications as necessary to fully specify the sliced range for every dimension. For example for a 4-dimensional tensor foo the slice foo[2, …, 5:8] implies foo[2, :, :, 5:8].
- new_axis_mask: a bitmask where bit i being 1 means the i th specification creates a new shape 1 dimension. For example foo[:4, tf.newaxis, :2] would produce a shape (4, 1, 2) tensor.
- begin_mask: a bitmask where a bit i being 1 means to ignore the begin value and instead use the largest interval possible. At runtime begin[i] will be replaced with
Output:
- Output output: Output object of StridedSliceGrad class object.
Result:
- std::vector(Tensor)
result_output: ATensorthe same type asinput.
Using Method
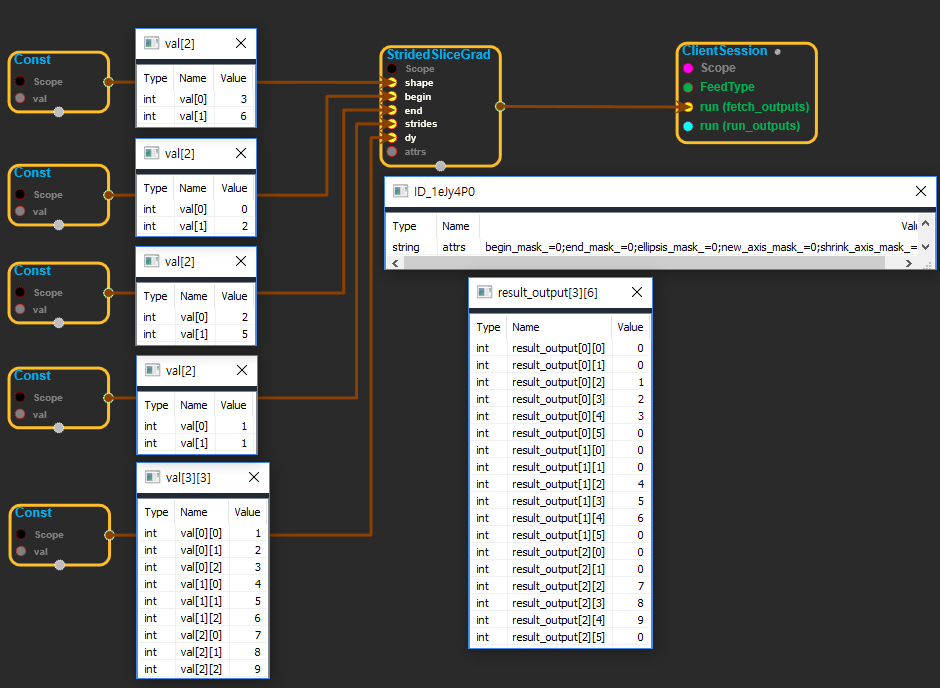 ※ dy로 들어온 tensor를 잘라서 shape에 들어온 값의 모양으로 만들어진 tensor에 집어 넣는다. end에서 begin을 뺀 값은 dy의 shape와 같아햐하며(예를 들어 dy의 shape가 [4, 3] 이라면 begin의 shape는 [2]이고 값은 [0, 1] end의 shape는 [2] 값은 [4, 4]가 되어야 한다.) shape 핀에 들어온 값은 이보다 크거나 같아야한다.
※ dy로 들어온 tensor를 잘라서 shape에 들어온 값의 모양으로 만들어진 tensor에 집어 넣는다. end에서 begin을 뺀 값은 dy의 shape와 같아햐하며(예를 들어 dy의 shape가 [4, 3] 이라면 begin의 shape는 [2]이고 값은 [0, 1] end의 shape는 [2] 값은 [4, 4]가 되어야 한다.) shape 핀에 들어온 값은 이보다 크거나 같아야한다.